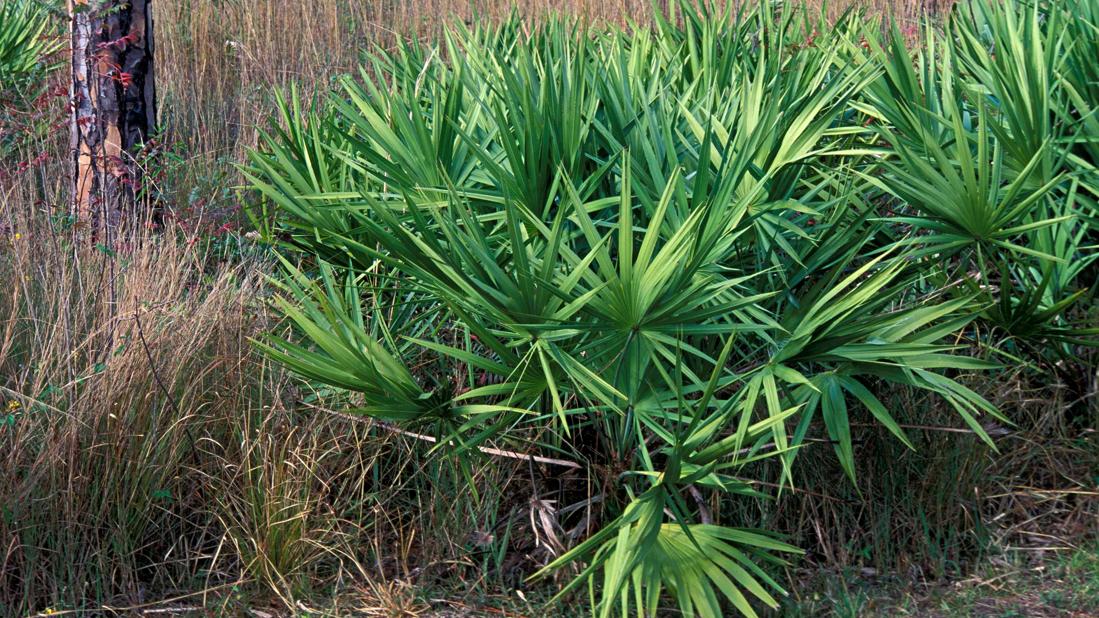
Ancient healers looked at scrubby thickets of saw palmetto and found medical purposes. They harvested berries from the plant and created treatments for urinary problems, reproductive issues and other maladies.
Thousands of years later, many still believe in the curative power of saw palmetto. Market projections suggest that sales of saw palmetto supplements could more than double between 2023 and 2033.
But here’s the question: Is there any evidence to suggest that saw palmetto actually delivers health benefits? We went looking for answers with preventive medicine specialist Robert Saper, MD, MPH.
What is saw palmetto?
Saw palmetto is a member of the palms botanical family that adds a tropical feel to sandy coastal areas, swamps and forests in the southeastern United States and other areas of the world. The slow-growing plant has a lifespan often measured in centuries.
More than 100 different chemical compounds exist in extracts made from the plant’s dark and olive-sized berries. The lengthy list includes fatty acids and sterols often found in dietary supplements.
Now, some of these compounds may affect how your body functions, which brings us to the historical use of saw palmetto and its current place in complementary and alternative medicine.
Use of saw palmetto
There’s evidence that the Egyptians used saw palmetto to treat urinary symptoms back in the 15th century BC. Native Americans in what is now Florida looked to saw palmetto to remedy prostate gland swelling, erectile dysfunction and testicular issues.
Fast-forward to current times and saw palmetto remains in rotation as a complementary or alternative treatment method for a range of health concerns, including:
- Prostate and urinary issues, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or enlarged prostate. (This is by far the most common health issue connected to saw palmetto use.)
- Hair loss.
- Migraine.
- Low testosterone.
“We’ve had medical herbalists recommending saw palmetto for thousands of years,” says Dr. Saper, Chair of Wellness and Preventive Medicine at Cleveland Clinic. “Given the history, there’s reasonable logic in believing there may be something behind it.”
Is saw palmetto effective?
The answer regarding the believed effectiveness of saw palmetto is different now than it would have been even 25 years ago, particularly when it comes to prostate health.
Large-scale studies funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) during the past two decades found that saw palmetto was no more effective in treating BPH than a placebo (or fake treatment). Other reviews reached similar conclusions.
There also is no clear evidence showing that saw palmetto is beneficial in addressing:
- Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland). Researchers found that people with chronic prostatitis who used saw palmetto for a year experienced no appreciable long-term improvement in symptoms.
- Prostate cancer. Lab studies have shown that saw palmetto may help fight cancer cell growth, but there haven’t been definitive findings regarding whether it reduces prostate cancer risk in people.
The above findings represent a departure from earlier thinking. Smaller studies in the 1980s and 1990s reinforced the belief that saw palmetto could be beneficial for various prostate issues, including BPH.
“We have a much clearer understanding after high-quality, systematic reviews that saw palmetto does not make a difference when it comes to treating issues of the prostate,” clarifies Dr. Saper.
Saw palmetto and other health claims
As mentioned, saw palmetto is sometimes touted as a remedy for other health issues. But little is known about the legitimacy of the claims given the lack of large-scale study, according to the NIH’s National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health.
Is saw palmetto safe?
While saw palmetto may not be able to resolve prostate problems or other health concerns, odds are taking the supplement won’t cause you any harm.
Reactions to saw palmetto are rare, says Dr. Saper, and if issues do appear, they tend to be mild. Reported side effects of saw palmetto have included headaches, plus feelings of dizziness and nausea.
Saw palmetto also isn’t known to interact poorly with medications. (That being said, it’s always best to talk to your healthcare provider before adding a supplement if you’re taking medication.)
In addition, it’s recommended that you not take saw palmetto if you are:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding (chestfeeding) given the lack of research on possible side effects.
- Within two weeks of a scheduled surgery due to concerns over increased bleeding risk.
Common dosage of saw palmetto
In clinical trials involving saw palmetto, the most common dosage was 160 milligrams twice a day, says Dr. Saper. The supplement is available in a variety of forms, including pills and tablets.
But know this: You might not be getting the amount of saw palmetto you think.
Government oversight of dietary supplements isn’t as stringent as prescription or over-the-counter medications, stresses Dr. Saper. That makes it difficult to know exactly what you’re getting in quality and concentration.
One study of saw palmetto supplements found that the actual amount of the herb varied from 3% to 140% of the stated dosage on the label.
Bottom line
Thousands of years of belief in the potential healing power of saw palmetto elevated the herb’s status within complementary and alternative medicine. Early research even hinted at some promise.
But more stringent research shows that saw palmetto may not be the answer to prostate issues and other health concerns.
“In a way, the cart came before the horse here,” says Dr. Saper. “Saw palmetto became quite popular, especially through marketing efforts, and then medical researchers had to play catch up to really understand what is happening.”
And in this case, research shows that saw palmetto falls short of its claimed benefits.
link